In recent years, the proliferation of smart technologies has revolutionized various sectors, with intelligent lighting systems standing at the forefront of this transformation. Among the numerous communication protocols designed for smart lighting, the DALI protocol has emerged as a widely adopted standard. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the DALI protocol and explore its significant applications within the smart lighting domain.
What is the DALI Protocol?
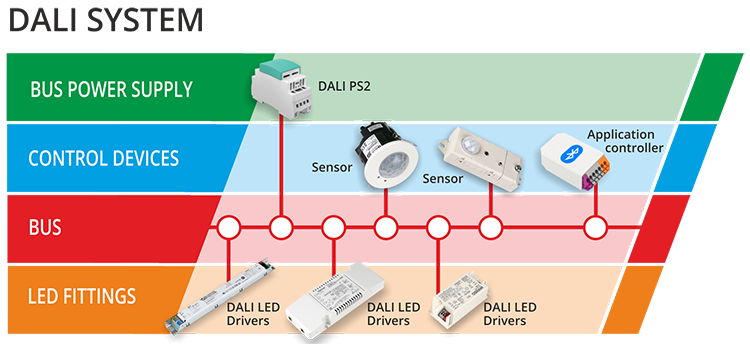
DALI, an acronym for Digital Addressable Lighting Interface, is an international standard communication protocol developed specifically for lighting control. It was introduced by the Digital Illumination Interface Alliance (DiiA) and defined under the IEC 62386 standard. The primary purpose of DALI is to enable digital communication between lighting control devices and electronic ballasts, drivers, and luminaires.
Unlike traditional analog controls, which use variable voltage or current to adjust lighting levels, DALI employs a digital two-wire bus system. This system allows multiple devices—up to 64 individually addressable ballasts and control devices—to communicate on a single control line. Each device can be assigned a unique address, making precise and flexible control of lighting systems possible.
Key Features of the DALI Protocol
- Digital Communication: DALI uses a digital signal for communication, which eliminates issues related to signal degradation and noise common in analog systems.
- Two-Wire Bus System: The protocol operates over a simple two-wire bus, simplifying wiring and installation.
- Addressability: Each device on the bus can be individually addressed and controlled. Up to 64 devices can exist on a single DALI bus.
- Bidirectional Communication: Devices can send status information back to the controller, enabling real-time monitoring and diagnostics.
- Interoperability: Compliance with IEC 62386 ensures that devices from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly.
- Scalability: The system supports grouping, scenes, and fade times, allowing for sophisticated control strategies.
How Does DALI Work?
The DALI protocol facilitates communication between controllers (such as lighting management systems or central control units) and the luminaires or ballasts. Commands are sent digitally over the two-wire bus to adjust parameters like on/off switching, dimming levels, color temperature (in tunable white or RGB systems), and scene recalls.
A typical DALI system consists of:
- DALI Controllers: Devices that send commands and interpret feedback.
- DALI Ballasts/Drivers: Electronic devices that regulate the power supplied to luminaires.
- Sensors and Input Devices: Occupancy sensors, daylight sensors, push buttons that can interface directly with the DALI bus.
Through this structured communication, users can configure dynamic lighting environments tailored to specific needs, such as energy savings, occupant comfort, or aesthetic effects.
Applications of the DALI Protocol in Smart Lighting
The DALI protocol has found widespread application across various smart lighting scenarios, due to its robustness, interoperability, and flexibility:
1. Commercial and Office Buildings
DALI enables centralized lighting control systems in office environments, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Lighting can be adjusted based on occupancy detection, daylight harvesting, or scheduling. For example:
- Occupancy-based Control: Lights automatically dim or switch off in unoccupied zones.
- Daylight Harvesting: Lighting levels adapt dynamically to available natural light to maintain desired illumination levels while conserving energy.
- Scene Setting: Preset lighting scenes can be activated for meetings, presentations, or different times of day.
2. Industrial Facilities
In industrial settings, lighting control needs to be reliable, scalable, and flexible. DALI offers:
- Robust Monitoring: Real-time diagnostics on lamp health, energy consumption, and faults enable preventive maintenance.
- Zonal Control: Different operational areas can be controlled independently or collectively, improving safety and efficiency.
- Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS): Through gateways, DALI systems can interface with broader facility management platforms.
3. Retail Environments
Retail stores benefit from the ability to tailor lighting atmospheres to enhance product displays and shopper experiences. DALI supports:
- Dynamic Lighting Scenes: Adjust lighting intensity and color temperature to highlight different merchandise or create mood changes.
- Energy Management: Efficient control reduces operational costs without compromising ambience.
- Event-Based Control: Lighting can be programmed to respond to specific events, store hours, or promotional activities.
4. Smart Home Applications
While DALI originated for commercial use, advancements and cost reductions have made it accessible for sophisticated residential lighting systems. Home automation platforms utilize DALI for:
- Multi-Room Lighting Control: Users can manage lights individually or through grouped controls.
- Integration with Voice Assistants and IoT: Through gateways, DALI systems can interface with popular smart home ecosystems.
- Personalized Scenes and Schedules: Customizable settings enhance user comfort and convenience.
5. Street and Outdoor Lighting
Municipalities employ DALI for smart street lighting networks, which require:
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Enable operators to manage and maintain lighting infrastructure efficiently.
- Adaptive Lighting: Adjust light levels based on traffic, time of day, or environmental conditions to enhance safety and reduce light pollution.
- Energy Savings: Automated dimming and switching reduce electricity consumption and carbon footprint.
Future Developments and Integration
The evolution of lighting technology, such as LED drivers supporting color tuning and Human-Centric Lighting (HCL), has spurred extensions to the DALI protocol. The latest generations support complex controls like color temperature adjustment (DALI-2 certification), enhanced communication speed, and integration with IP-based networks.
Moreover, DALI is increasingly interoperable with other protocols, such as KNX, BACnet, and Zigbee, enabling holistic building automation ecosystems.
Conclusion
The DALI protocol is a foundational component in the development of intelligent lighting systems. By providing a reliable, flexible, and interoperable digital communication interface, it facilitates precise control, monitoring, and optimization of lighting environments across a broad spectrum of applications.
From commercial offices and industrial complexes to retail spaces and smart homes, the advantages of DALI-driven lighting solutions include improved energy efficiency, enhanced occupant comfort, and simplified system management. As lighting technology continues to advance and integrate with broader smart infrastructure, the role of DALI protocols is expected to remain pivotal in the quest for smarter, sustainable, and user-centric lighting environments.