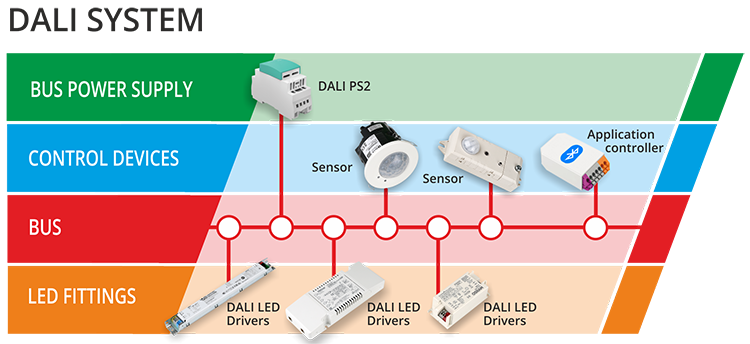
In the rapidly evolving landscape of intelligent lighting systems, DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) has emerged as a global standard for digital lighting control. For designers, engineers, and installers working with DALI-compatible LED fixtures, selecting the right DALI power driver is a critical step that significantly impacts system performance, energy efficiency, and user experience. This article delves into the essential factors and considerations involved in choosing an appropriate DALI power driver, designed to guide professionals in making informed decisions.
Understanding DALI and the Role of the Power Driver
Before exploring how to select a DALI power driver, it is important to understand what DALI is and why the driver plays a pivotal role.
What is DALI?
DALI is a standardized protocol (IEC 62386) for digital communication between lighting control devices such as ballasts, drivers, sensors, and control panels. It allows for individual or group addressing of luminaires, granular dimming control, scene setting, and status monitoring, enabling sophisticated lighting solutions in commercial, residential, and industrial environments.
What is a DALI power driver?
A DALI power driver powers the LED luminaire while integrating the DALI communication interface. It converts input voltage to the required DC current for LEDs and interacts with the DALI network for commands such as on/off switching and dimming. Unlike conventional drivers without communication, DALI drivers provide digitally addressable control and feedback capabilities, which are vital for modern smart lighting systems.
Key Factors in Selecting a DALI Power Driver
Selecting the right DALI power driver hinges on evaluating multiple technical parameters and alignment with your system requirements. Below are the primary aspects to consider:
1. Compatibility with LED Loads
- Output Current and Voltage:
Confirm that the driver supports the LED modules’ forward voltage and current requirements. DALI drivers come in various voltage and current ratings (e.g., constant current drivers with outputs ranging from 350mA to 1050mA or more). Correct matching ensures optimal LED performance and longevity. - Power Range:
Calculate the total wattage needed for your application and choose a driver that can supply this power continuously. Oversizing the driver slightly is advisable for reliability but excessive oversizing can lead to inefficiencies.
2. Dimming Capabilities
- Type of Dimming:
DALI supports 8-bit (256 levels) and 16-bit (65,536 levels) dimming depth. Depending on your project’s precision requirements, select a driver compatible with your desired dimming resolution. - Dimming Curve:
Different applications may prefer different dimming curves, including linear, logarithmic, or customized curves to suit human visual perception. Check if the driver offers configurable dimming profiles. - Smoothness and Flicker:
High-quality DALI drivers provide flicker-free dimming at low light levels, important for user comfort and compliant with standards such as IEEE 1789.
3. Network and Addressing Features
- Number of DALI Addresses Supported:
Drivers conform to DALI-2 standard often support multiple short addresses and can participate in groups/scenes. Ensure the driver supports the addressing scheme you need. - DALI Version Compliance:
Ensure your driver complies with the DALI-2 standard (IEC 62386-101 to 207) which improves interoperability, includes device type declarations, and adds enhanced diagnostics. - Broadcast and Command Functions:
Check how drivers respond to broadcast commands and whether they support firmware updates over DALI if needed.
4. Input Voltage Range and Power Supply
- Input Voltage Compatibility:
Make sure the driver’s input voltage matches your supply environment, commonly 220-240V AC for most regions, but also available for 110V or other voltages. - Power Factor and Efficiency:
A high power factor (typically above 0.9) and high efficiency (greater than 85%) reduce energy loss and utility costs, while minimizing harmonic distortion on the supply.
5. Thermal Management and Environmental Specifications
- Operating Temperature Range:
Select drivers with specifications suited to the installation location. For harsh or outdoor environments, consider drivers with wider temperature tolerance and protection ratings. - IP Rating and Protection:
For damp or dusty environments, an IP65 or higher rating driver ensures durability. Also, check for protections including overvoltage, overcurrent, short circuit, and surge protection compliant with safety standards.
6. Certification and Standards Compliance
Ensure that the selected DALI driver holds relevant certifications such as CE, UL, RoHS, CCC, or other regional standards to guarantee safety, quality, and regulatory compliance.
7. Additional Features
- Diagnostics and Feedback:
Advanced drivers may offer real-time operational data such as power consumption, operating hours, temperature, and fault alerts accessible through the DALI network. - DALI Type and Integration:
Some drivers support DALI Type 8 (constant current LED drivers with high-end trim), enabling more precise current control for improved color consistency. - Physical Size and Form Factor:
The driver should fit comfortably within the luminaire or fixture housing. Slim, compact designs facilitate integration in tight spots.
Common Types of DALI Drivers
To help match your needs, here is a brief overview of common driver types:
- Standard DALI LED Drivers:
Basic models offering on/off and dimming via DALI. Suitable for most conventional LED fixtures. - DALI DT8 Drivers:
Include color control functionalities to manage tunable white LEDs or RGB/RGBW applications. - Emergency DALI Drivers:
Integrated emergency lighting support that can be centrally controlled and tested using DALI commands. - DALI Multi-Driver Solutions:
Designed for high-power luminaires or modular systems where multiple drivers communicate under one address.
Selecting a Supplier and After-Sales Support
Choosing a reputable manufacturer or supplier is vital. Factors include:
- Comprehensive technical support and application engineering assistance.
- Availability of testing reports, firmware updates, and documentation.
- Warranty policies and replacement procedures.
- Compatibility guarantees with major DALI control systems.
Conclusion
Selecting the right DALI power driver is a crucial decision that balances technical performance, system compatibility, and long-term reliability. By carefully evaluating the LED load requirements, dimming capabilities, communication features, certifications, and environmental suitability, lighting professionals can ensure robust and efficient digital lighting installations.
As the industry gravitates toward smarter, networked lighting ecosystems, investing time in understanding driver specifications and DALI standards equates to future-proofing your projects and delivering superior lighting experiences.
About the Author:
Lifud is a lighting technology specialist with extensive experience in LED driver design and digital lighting control systems. Passionate about energy-efficient and intelligent lighting solutions, Lifud frequently publishes insightful guides on lighting technologies and industry trends.
By applying the principles outlined in this guide, you can confidently select the ideal DALI power driver tailored to your project requirements and embrace the benefits of intelligent lighting control.