In the rapidly evolving landscape of lighting technology, smart lighting systems have emerged as a pivotal element driving innovation in both residential and commercial sectors. Among various smart lighting protocols, DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) stands out as a standardized communication system widely adopted for intelligent lighting control. As urbanization accelerates and sustainability gains prominence, the DALI smart lighting market is poised for significant growth. This blog post delves into the market prospects of DALI smart lighting, examining its technological advantages, current applications, industry trends, and future outlook.
Understanding DALI and Its Role in Smart Lighting
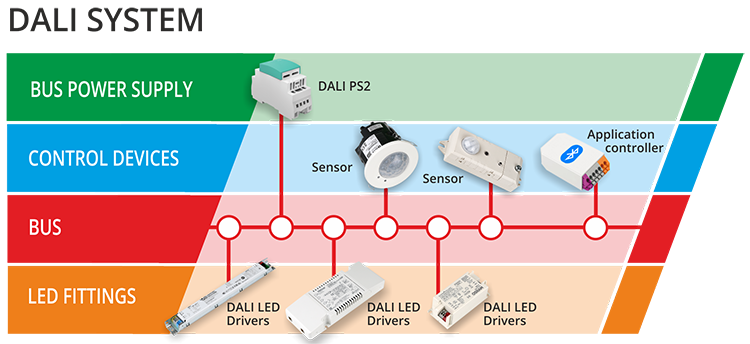
DALI is an international standard (IEC 62386) developed specifically for lighting control systems. Unlike traditional wiring systems where each light is hardwired to a separate switch, DALI enables digital communication between lighting devices and control units via a simple two-wire bus system. Each lighting fixture can be individually addressed and controlled, allowing for precise dimming, grouping, and scene-setting.
Smart lighting based on DALI integrates this protocol with modern Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, enabling remote monitoring, automated adjustments based on environmental conditions, and integration with building management systems (BMS). This combination renders DALI smart lighting a versatile and flexible solution for enhancing lighting efficiency, comfort, and sustainability.
Technological Advantages Fueling Market Growth
- Interoperability and Standardization: DALI is a globally recognized open standard, ensuring compatibility across manufacturers and devices. This reduces vendor lock-in risks and encourages broader adoption by system integrators and end users.
- Scalability and Flexibility: DALI systems can manage up to 64 devices per network line, with the ability to create complex groupings and scenes. This scalability suits everything from small office buildings to large commercial complexes and industrial plants.
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Integrating sensors such as occupancy detectors and daylight harvesters into a DALI network allows dynamic lighting adjustments, significantly reducing energy waste without compromising occupant comfort.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: The simple bus wiring reduces installation complexity and costs compared to conventional systems. Additionally, centralized control and diagnostics facilitate preventive maintenance and reduce operational downtime.
- Compatibility with Advanced Controls: DALI systems can be integrated with wireless technologies, cloud platforms, and AI-driven analytics, opening avenues for smarter building automation and data-driven energy management.
Current Market Applications of DALI Smart Lighting
- Commercial Buildings: Offices, retail spaces, hotels, and shopping malls leverage DALI smart lighting to enhance ambiance, improve occupant productivity, and achieve energy certifications such as LEED or BREEAM.
- Industrial Facilities: Warehouses and factories use DALI-controlled lighting to boost visibility, safety, and reduce operational costs via automation.
- Public Infrastructure: Street lighting, transportation hubs, and educational institutions adopt DALI solutions to enable centralized management, improve public safety, and reduce municipal energy expenses.
- Healthcare and Hospitality: These sectors benefit from tunable lighting features supported by DALI, which can aid circadian rhythm adjustments and promote wellness.
Market Trends and Drivers
Several key trends underlie the positive market prognosis for DALI smart lighting:
- Sustainability and Regulatory Pressure: Global initiatives targeting carbon neutrality and strict energy efficiency regulations incentivize the adoption of smart lighting solutions capable of reducing electricity consumption.
- Growing Smart City Projects: Urban centers worldwide are investing in smart infrastructure, with intelligent lighting as a foundational element. DALI’s standardization and interoperability fit well into these large-scale deployments.
- Integration with IoT and Building Automation: The convergence of lighting with IoT devices and BMS creates increased demand for flexible and IP-based DALI systems, such as DALI-2, which support advanced control devices and diagnostics.
- Technological Innovation: Advances in LED technology, wireless integration (e.g., DALI wireless solutions), and cloud-based management platforms are expanding the functional scope of DALI smart lighting systems.
- Cost Reductions and Increased Accessibility: As technology matures, hardware costs decrease, making DALI smart lighting more accessible to smaller businesses and residential customers.
Challenges Facing the Market
While the prospects are promising, certain challenges remain:
- Competition from Alternate Protocols: Other lighting control standards such as Zigbee, Bluetooth Mesh, and proprietary solutions offer wireless ease-of-use that may challenge DALI’s traditionally wired approach.
- Complexity of Integration: Retrofitting existing buildings with DALI systems involves upfront costs and design complexities that may hinder adoption.
- Education and Awareness: Market penetration depends heavily on educating architects, engineers, and facility managers about the benefits and implementation strategies for DALI smart lighting.
Future Outlook and Market Forecast
Industry reports forecast a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the smart lighting market exceeding 15% over the next decade, with DALI-based solutions capturing a significant share due to their robustness and standardization. The introduction of DALI-2 — an enhanced protocol version with expanded device types and improved interoperability — further strengthens market confidence.
Moreover, the synergies between DALI smart lighting and emerging technologies like 5G, AI, and edge computing point toward increasingly intelligent, responsive, and adaptive lighting environments. These developments will enable smarter energy management, predictive maintenance, and enriched occupant experiences.
Conclusion
The market prospects for DALI smart lighting are robust, supported by strong technological foundations, regulatory momentum, and expanding application domains. Its standardized, scalable, and energy-efficient nature positions DALI as a key enabler in the broader smart building and smart city ecosystems. While challenges remain, ongoing innovation and growing stakeholder awareness are likely to drive widespread adoption, making DALI smart lighting a cornerstone of future lighting control solutions.
Stakeholders—including lighting manufacturers, system integrators, policy makers, and end users—should closely monitor advancements in DALI technology and leverage its capabilities to capitalize on this rapidly growing market. Investing in DALI smart lighting not only enhances operational efficiency and occupant satisfaction but also contributes meaningfully to global sustainability goals.